EDITORIAL
On February 27, 2025, in Moscow, within the framework of the XVIII International Congress "Drug development and registration", a round table "Research of Medicinal Plant Raw Materials" was held for the first time.
PHARMACEUTICAL BOTANY
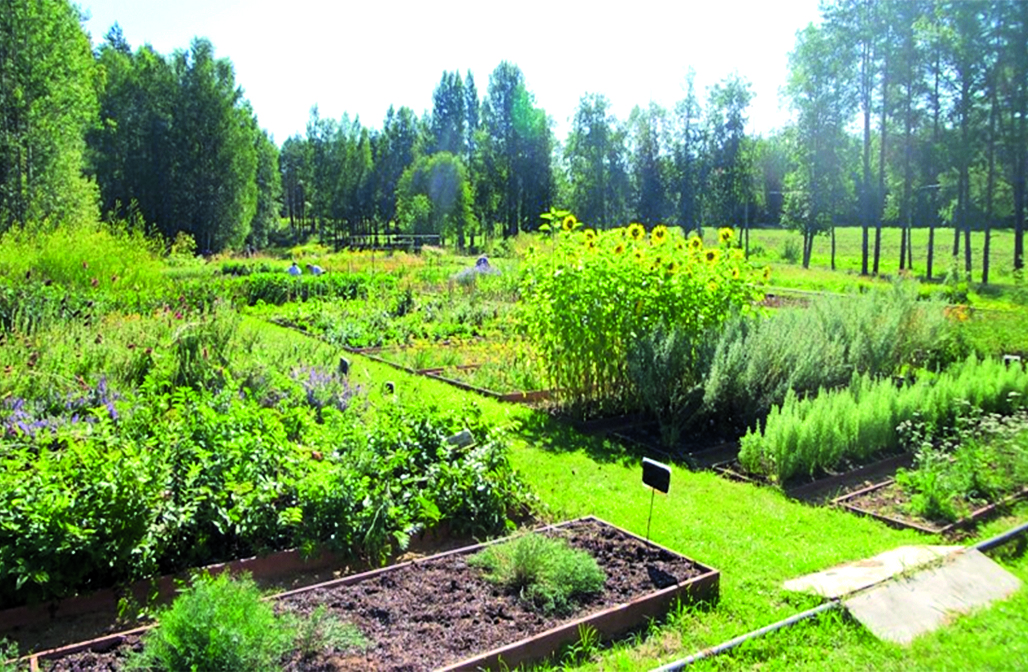
Introduction. The nursery of medicinal plants of the St. Petersburg State Chemical and Pharmaceutical University is a unique collection of medicinal plants for North-West Russia. More than 200 species of plants used in medicine are cultivated on an area of about 40 hectares. The nursery serves as a basis for scientific practices of students in botany and pharmacognosy, as well as for scientific studies in pharmacognosy and phytochemistry, agrotechnological experiments and obtaining biomaterials for in vitro cultivation.
Text. The nursery was founded in 1952 for education and scientific research of the Chemical-Pharmaceutical Institute in Karelia, on the shore of Lake Silande. On a small area, it was possible for students to study almost all phytocenoses typical of the Karelian Isthmus. In addition, the favorable location of the nursery allows cultivating plants of more southern regions with plants of a temperate climate. The collection area of approximately 1.5 hectares contains official species as well as species that are promising from the point of view of introduction into scientific medicine; woody and ornamental plants are collected in separate areas. The collection contains more than 200 species of living plants and is constantly expanding. On the basis of the nursery, summer educational practice in botany and pharmacognosy is carried out with students of the SPCPU, of the Perm State Pharmaceutical Academy, Pyatigorsk Medical and Pharmaceutical Institute, Lugansk State Medical University, the Medical Faculty of St. Petersburg State University, the Vitebsk Medical Faculty of the University and the Belarusian Medical University (Minsk), South Kazakhstan Medical Academy, Tashkent Pharmaceutical Institute; excursions and scientific and practical seminars on medicinal plant growing are held. Objects for phytochemical, pharmacognostic, biotechnological research, as well as for scientific purposes are grown and harvested in the nursery.
Conclusion. For further development of the nursery, a concept was developed for the creation of the Botanical Garden of Medicinal Plants of SPCPU on its basis, the tasks of which will be the cultivation, study of medicinal plants and popularization of knowledge about them. It is planned to develop the infrastructure of the nursery, create new exhibition and resource areas, and develop routes for organizing environmental processes for various phytocenoses. Thus, the SPHFU nursery is a valuable resource for both educational activities and scientific research, contributing to the development of science and practice in the context of conservation and moderate use of resources.
Introduction. Astragalus varius S.G. Gmel. is a species from the large genus Astragalus L. (Fabaceae), the herb of which contains flavonoids, saponins, vitamins, phenolic carboxylic acids, triterpene saponins and other compounds. Extracts from the herb have antioxidant, antimicrobial and diuretic properties. Microdiagnostic features of the herb of A. varius have been studied previously, but their quantitative characteristics are missing.
Aim. Determination of morphometric characteristics of microdiagnostic features of the herb A. varius.
Materials and methods. The analyzed object of the study was the herb of A. varius S.G. Gmel., harvested in July 2023 in different areas of the Saratov region. Macro- and microscopic analysis was performed using a Mikromed MS-1 stereomicroscope (China), a ZEISS Plan-Apochromat microscope (Germany) in accordance with the requirements of OFS.1.5.3.0003 «Technique of microscopic and microchemical study of medicinal plant materials and medicinal herbal preparations» of the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation, XV edition. Microphotographs were edited using Photoscape 3.7. Morphometry was performed using a ZEISS Plan-Apochromat microscope (Germany). The unit of measurement was a micrometer. For each structure, 10 measurements were performed (n = 10). Statistical processing of the obtained data was carried out in Excel (ver. 2016, Microsoft, USA). The data in the tables are presented as mean values with standard deviation.
Results and discussion. As a result of the conducted studies, it was established that the macro- and microdiagnostic features of the analyzed species correspond to our description presented earlier. For the first time, morphometric characteristics of the microdiagnostic features of the herb of A. varius (length and width of epidermal cells, diameter of the stomata of the leaf, stem, calyx and corolla; length and width of T-shaped hairs; ratio of the shoulders of T-shaped hairs) were established.
Conclusion. Quantitative characteristics of microdiagnostic features of the herb of A. varius have been identified. The results of experimental studies complement the data of scientific literature and can be used to confirm the authenticity of this type of raw material.
ANALYSIS AND STANDARDIZATION OF MEDICINAL PLANT MATERIALS
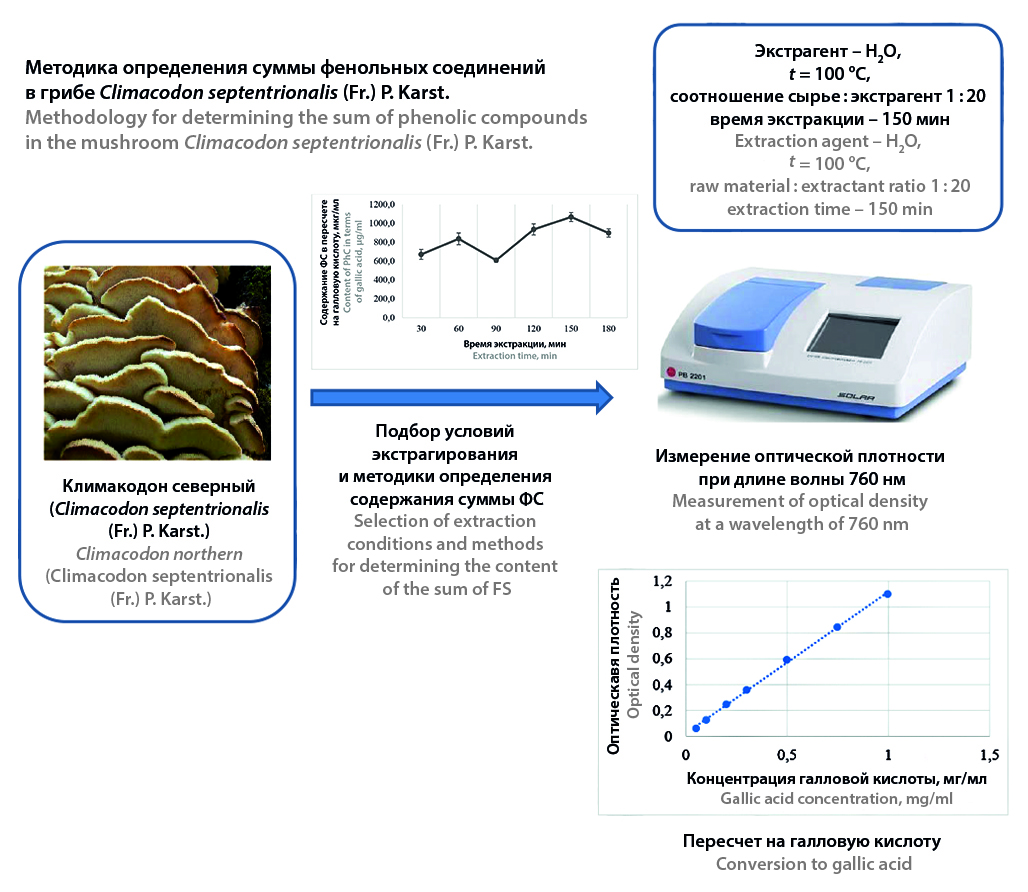
Introduction. The parasitic fungus Climacodon septentrionalis (Fr.) P. Karst. has been little studied at the moment, but it is known to have antioxidant activity, which can be used in medicine. Only one medicinal product of fungal origin and a number of biologically active food supplements are registered in the Republic of Belarus. There is no information on the optimal methods and techniques for obtaining an extract from raw materials of fungal origin with the maximum possible content of phenolic compounds, as well as methods for their determination.
Alm. To develop a method for determining the content of phenolic compounds in the fungus Climacodon septentrionalis.
Materials and methods. The object of the study was the fruiting bodies of the northern Climacodon mushroom (C. septentrionalis), grown in natural conditions and stored at a temperature of –18 °C. The following reagents were used in the study: Folin – Chiocalteu reagent (LLC "Analit Komplekt", Russia), anhydrous sodium car-bonate (reagent grade, LLC "JSC REAKHIM", Russia), technical ethyl alcohol Extra-M 96.41 %, purified water; gallic acid standard (98 %, Acros Organics BVBA, Belgium); equipment: Explorer EX125D analytical scales, SOLAR PB 2201 spectrophotometer, Good-helper ES-10P10 electric hotplate, WB-12 water bath, AE-25 electric water dis-tiller.
Results and discussion. The optimal method for extracting phenolic compounds from northern Climacodon is extraction with water at a temperature of 100 °С and a raw material : extractant ratio of 1 : 20 for 150 minutes once, draining the liquid into a separate closed container, leaving it to cool at room temperature, filtering through a cotton swab, bringing it to the original volume with water if necessary. When determining the amount of phenolic compounds in terms of gallic acid, it is recommended to use 0.10 ml of the extract, 0.45 ml of Folin – Ciocalteu reagent, stirring, adding 5.25 ml of 10 % sodium carbonate solution, stirring, reaction time – 16 minutes, measuring the optical density at a wavelength of 760 nm.
Conclusion. The concentration of the sum of phenolic compounds in terms of gallic acid in the obtained extract is 202 ± 5 μg/ml or the mass fraction when converted to the wet weight of C. septentrionalis is 0.41 ± 0.01 %.
Introduction. In official medicine, the fruits of bird cherry (Padus avium Mill.) are used in the form of a decoction, which have an astringent effect due to the presence of tannins. The study of other non-pharmacopoeial parts of medicinal plants is relevant today. Modern pharmaceutical practice is aimed at conducting scientific research on the search for new types of plant raw materials. In this case, it is interesting to study the bark of the bird cherry as a promising medicinal plant raw material.
Aim. To study the composition and quantify the content of biologically active substances (BAS) in bird cherry bark.
Materials and methods. The bark of the bird cherry, collected during the sap flow and dried in a natural way, was chosen as the object of the study. The qualitative composition of BAS was studied by chemical reactions, as well as by chromatography in a thin layer of sorbent (TLC). Titrimetric methods and capillary electrophoresis were chosen to assess the content of BAS.
Results and discussion. Tannin, gallic acid, ascorbic acid, citric acid, and malic acid have been identified in the bark of the bird cherry. No flavonoids were detected. In the course of the work, a quantitative analysis of ascorbic acid (0,40 ± 0,04 %), tannins (7,80 ± 0,03 %), organic acids (7,40 ± 0,04 %) and water-soluble vitamins (C and group B) was carried out, the total content of which was 0,533 %.
Conclusion. The content of biologically active substances in bird cherry bark has been studied. The highest amount of tannins and organic acids was found in the raw materials. Due to its chemical composition, bird cherry bark can be used as a source of biologically active compounds in official medicine.
Introduction. Tuberculosis is a socially significant disease both in the territory of the Russian Federation and worldwide. The high resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and the high toxicity of existing chemotherapeutic drugs necessitate the development of new medications. Plant-based medicinal agents are promising for complex tuberculosis therapy, as they can support the patient’s weakened body, reduce the side effects of chemotherapeutic drugs, and strengthen lung tissue.
Aim. To develop the plant-based medicinal composition for the complex therapy of tuberculosis.
Materials and methods. Fourteen pharmacopoeial types of medicinal plant raw materials and three plant-based compositions derived from them were analyzed. The studies were conducted according to the methodologies outlined in the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation (15th edition).
Results and discussion. Based on scientific data, three compositions of plant-based formulations for the complex therapy of pulmonary tuberculosis were proposed. The quantitative content of the main groups of biologically active substances (BAS) – polysaccharides, tannins, flavonoids, and ascorbic acid – was studied in 14 types of medicinal plant raw materials and three plant-based compositions. A plant-based composition variant with the maximum BAS content was identified. The mutual influence of components on the extraction efficiency of BAS from the raw materials was established.
Conclusion. The plant-based medicinal composition for the complex therapy of tuberculosis was developed, and the main groups of BAS in its hydrophilic fraction were quantitatively determined.
BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY OF NATURAL SUBSTANCES
Introduction. Medicinal plants, the complex of phytocomponents of which includes vitamins, polysaccharides and simple sugars, organic acids, carotenoids, polyphenolic compounds such as: flavonoids, oxycinnamic acids, anthocyanins, lignans and tannins, have powerful antioxidant activity (AOA) and significant potential in the fight against active oxygen species. Low molecular compounds along with a group of specialized enzymes form the antioxidant system of the plants themselves, which is necessary to neutralize active oxygen species and protect cells from oxidative stress. Sea buckthorn leaves, on the one hand, have long been known as a raw material for pharmaceutical factories, on the other hand, according to literary data, have prospects for expanding the range of pharmaceutical products based on them, which can potentially have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, astringent, capillary-protective and venotonic effects.
Aim. The aim of the work was a comparative study of the antioxidant activity of sea buckthorn leaves at different periods of their development using different methods.
Materials and methods. The object of the study is sea buckthorn leaves. The AOA of the raw material and aqueous dosage forms based on it was assessed using a well-known spectrophotometric technique. The content of ascorbic acid in the leaves was determined using the titrimetric technique presented in Ph.A.2.5.0106.18 of the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation, 15th edition, «Rose fruсtus». The AOA of the leaf decoction was determined using the also known permanganometric method according to Maksimova et al.
Results and their discussion. The article presents the results of determining the total content of antioxidant substances (BAS-AO) in terms of ascorbic acid and the total antioxidant activity (AOA) of sea buckthorn leaves harvested in different periods of development in the Central Black Earth Region of the Russian Federation, using the method of differential spectrophotometry. The highest values were characteristic of the raw materials of the phenophase corresponding to the period of full ripening of the fruits. Analysis of the correlation of the obtained AOA values with the content of ascorbic acid, tannins and flavonoids in the leaves showed that the antioxidant effect is largely determined by the accumulation of ascorbic acid in them. As part of expanding the areas of use of sea buckthorn leaves in pharmacy and medicine, it was found that in a decoction, as one of the potential dosage forms based on raw materials, the total content of substances that prevent oxidation, expressed in the equivalent of ascorbic acid, was 17.50 mg%.
Conclusion. The method of differential spectrophotometry was used to determine the AOA of sea buckthorn leaf extracts harvested in different periods of development, and it was found that the highest values were characteristic of the raw material of the phenophase corresponding to the period of full ripening of the fruits. The analysis of the correlation of the obtained AOA values, which is the sum of the activities of different groups of biologically active substances-AO, pre-sent in one extract, with the content of ascorbic acid, carotenoids, leucoantho-cyanins, tannins and flavonoids in the leaves showed that the antioxidant effect is largely determined by the accumulation of ascorbic acid and carotenoids in them. In the decoction, as one of the potential medicinal forms based on the raw material, the total content of substances that prevent oxidation, expressed in the equivalent of ascorbic acid, was 17,50 mg%.