EDITORIAL
In February 2026, Moscow will host the annual two-day congress "Drug development and registration". The congress's topics traditionally cover all key stages of a drug's life cycle, from development to post-registration studies.
CHEMISTRY OF NATURAL COMPOUNDS
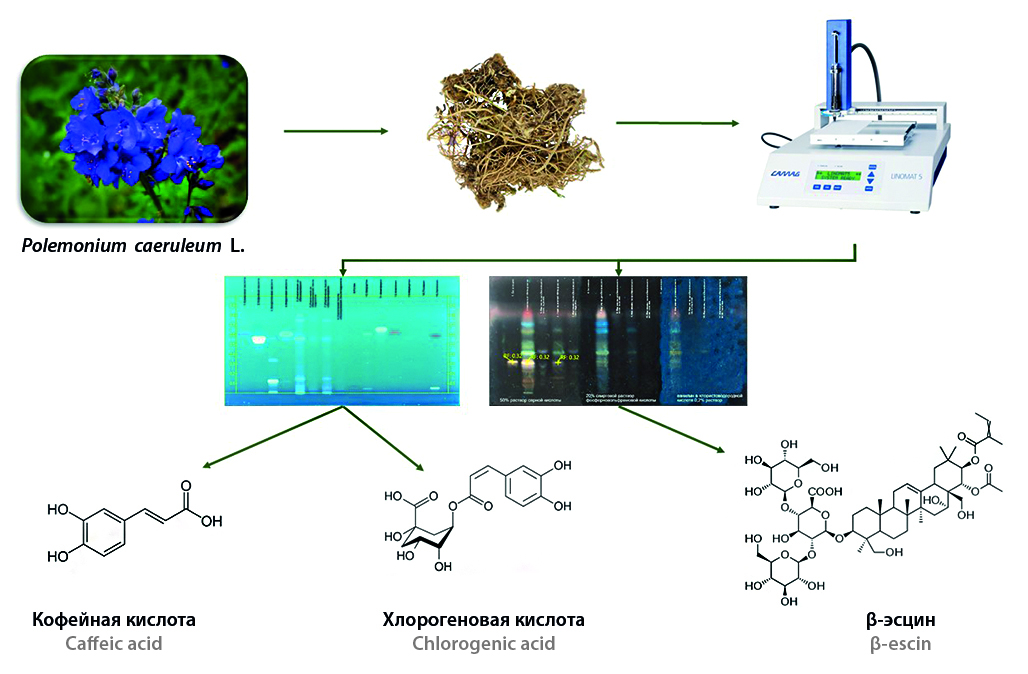
Introduction. Polemonium caeruleum L. is a promising medicinal plant with multivector therapeutic effect. However, the limited data on its phytochemical composition makes it difficult to develop modern medicines based on it. The need for a detailed study of chemical composition and optimization of standardization methods is due to the growing interest in the use of bluegill for the treatment of diseases of the nervous system and the demand of the socium for neurotropic phytodrugs.
Aim. Conducting HPTLC analysis for phytochemical screening of blue cornelian fern extracts.
Materials and methods. This study utilized samples of rhizomes and roots of Polemonium caeruleum, collected in the Leningrad region. Standard samples of flavonoids, hydroxycinnamic acids, and β-aescin were used for phytochemical analysis. Purified (preliminary defatting with chloroform in a Soxhlet apparatus) and crude extracts were obtained from the raw material by extraction with 80 % ethanol using an ultrasonic bath. HPTLC analysis was performed on Silica gel 60 F254 plates in the following solvent systems: toluene – ethyl acetate – formic acid – water (for phenolic compounds) and n-butanol – acetic acid – water (for saponins). Detection was performed under UV light and using detection reagents.
Results and discussion. On the basis of a HPTLC-analysis carried out in roots with bluegill roots, chlorogenic acid has been identified. It has been established that the procedure of degreasing the raw material leads to a decrease in the content of phenolic compounds, and acid hydrolysis significantly changes their chromatographic profile. For the detection of saponins, the ineffectiveness of the method regulated by the GF of the Russian Federation is shown, and a solution of 50 % sulfuric acid was proposed as the detecting agent, which allowed to uniquely identify β-aescin (Rf = 0.32). The chromatographic analysis revealed a complex multicomponent composition of extractions, including several groups of BASs.
Conclusion. In view of the growing need for effective and safe phyto-drugs with a neurotropic and expectorant action, as well as insufficient knowledge of the chemical composition of bluegill, its complex phytochemical screening was carried out. By HPTLC method in the underground organs of the plant was identified chlorogenic acid, and also confirmed the presence of a marker saponine – β-aescin, for the detection of which the selection of the detecting agent is optimized. The data obtained fill a lack of modern scientific knowledge about this type of raw material and form the basis for the development of standardized LDC based on it.
HERBAL TECHNOLOGY
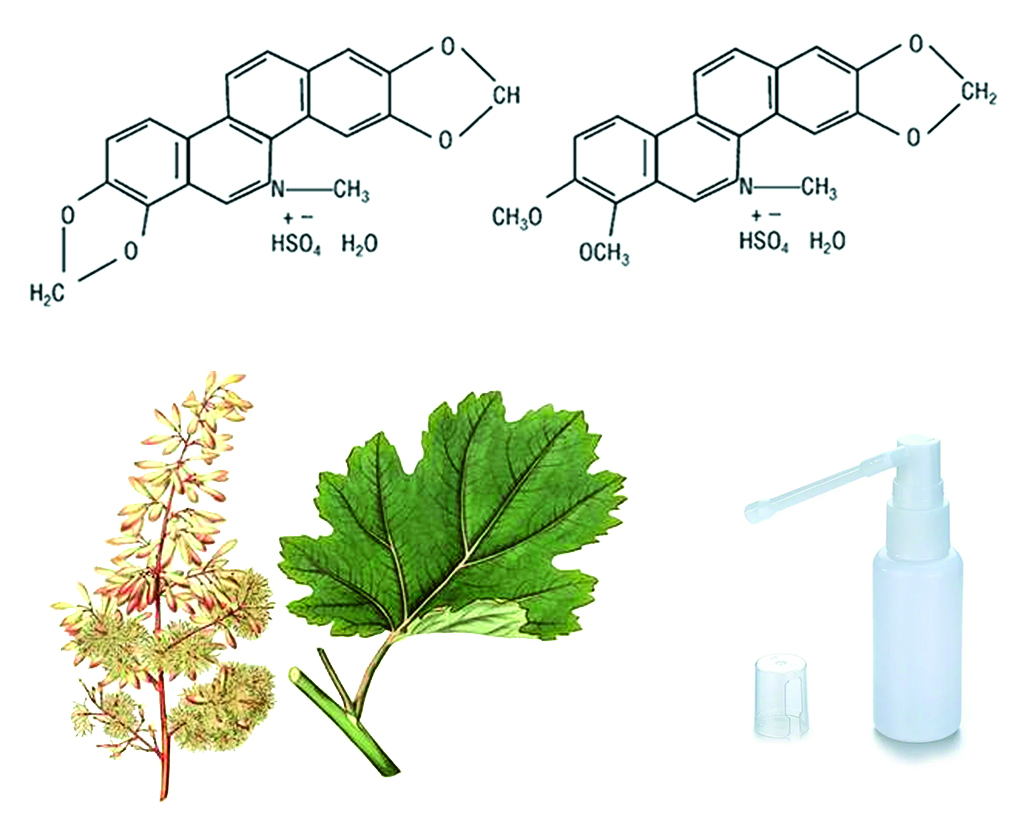
Introduction. The use of antibiotics in the treatment of infectious diseases has led to significant achievements in medicine, but the problem of microbial resistance to antibiotics and the need to develop new antibacterial drugs remain extremely relevant today. One of the promising areas in combating this problem is the search for antimicrobial substances among plant raw materials. This study focused on the substance sangviritrin, which has pronounced antimicrobial properties.
Aim. The aim of the study was to investigate the technological and therapeutic characteristics of an oral dosed spray of sangviritrin for the treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity.
Materials and methods. The object of the study was an oral metered spray of sangviritrin, packaged in 30 ml light-protective glass bottles (LLC "TС "BELAND", Russia) 30 ml polyethylene bottles (LLC "SRP Group", Russia), and LF plastic nozzles (Shenzhen Bona Pharma Technology Co., Ltd., China). The minimum filling volume of the bottle, requirements for primary and secondary pumping, and requirements for nozzle cleaning were determined. The substances extracted from the packaging were studied using high-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS), gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). The stability of the spray was determined in long-term and accelerated tests. The antimicrobial activity of the sangviritrin spray was determined for 21 strains of microorganisms.
Results and discussion. The minimum filling volume of the vial was 31 ml. It was shown that there are no requirements for priming the spray dispenser, cleaning the dispenser after use, or shaking. Extractable substances from Russian-made polyethylene bottles were studied using HPLC-MS, GC-MS, and IS-MS methods. The experiment demonstrated that these substances are present in concentrations below the threshold value and cannot adversely affect the safety of the drug. Long-term studies have demonstrated the stability of the developed dosage form for 12 months, and accelerated testing has determined the shelf life of the spray to be 2 years. An in vitro study of the antimicrobial activity of sangviritrin spray using a spot test showed its effectiveness against 18 strains of bacteria and three strains of Candida fungi.
Conclusion. The developed dosage form is stable during storage, methods for controlling its quality have been determined, the choice of packaging is justified, and this drug is promising for use in the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity.
MEDICINAL PLANT GROWING. PROCUREMENT OF MEDICINAL PLANT RAW MATERIALS. RESOURCE SCIENCE
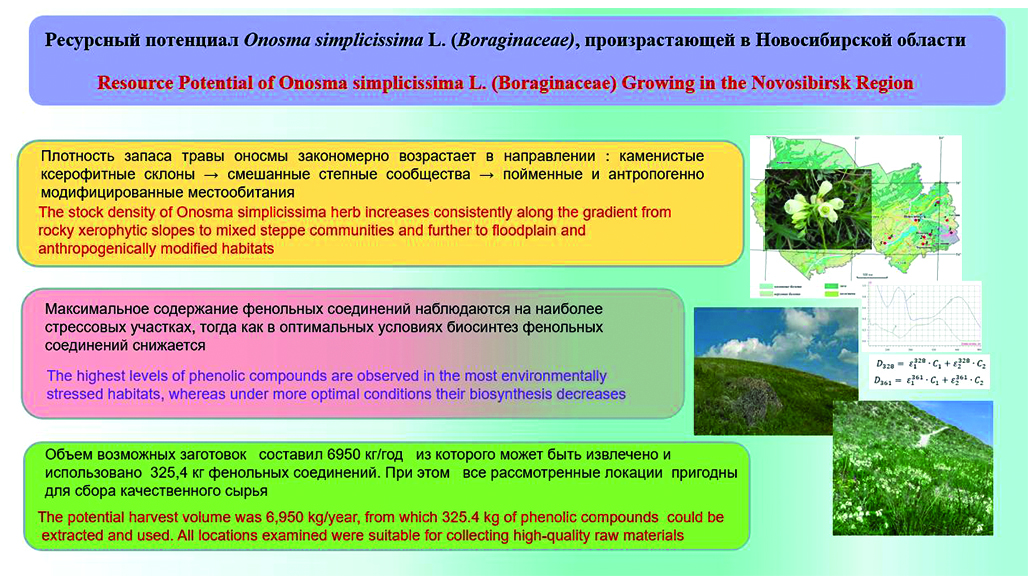
Introduction. Wild medicinal plants represent an important source of biologically active compounds widely used in pharmaceutical practice. Species of the genus Onosma L. (Boraginaceae) are characterized by high ecological plasticity and significant pharmacological potential associated with the accumulation of phenolic compounds. Onosma simplicissima L., widely distributed in the steppe and forest-steppe landscapes of Western Siberia, is considered a promising source of flavonoids and oxycinnamomic acids. However, an adequate assessment of its resource potential requires consideration of both biomass reserves and environmentally driven variability of the phytochemical profile.
Aim. To perform a comprehensive assessment of the resource potential of Onosma simplicissima L. within the Novosibirsk Region and to determine the influence of habitat conditions on the content of phenolic compounds in herb raw material.
Materials and methods. The study was conducted on the aerial parts of O. simplicissima collected at the flowering stage from nine locations in the Novosibirsk Region. Resource characteristics were evaluated using the model plant method with calculation of biological and exploitable reserves as well as potential annual harvest volumes. The total content of oxycinnamomic acids and flavonoids was determined by spectrophotometry and expressed as rosmarinic acid and rutin equivalents, respectively. Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t-test at a confidence level of P = 95 %.
Results and discussion. A pronounced spatial heterogeneity of biomass density and phenolic compound content was revealed depending on habitat conditions. Maximum biomass values were observed in floodplain and anthropogenically transformed habitats, whereas the highest concentrations of phenolic compounds were recorded in xerophytic rocky slopes. An inverse relationship between biomass accumulation and phenolic metabolite content was established, reflecting the adaptive strategy of the species under abiotic stress.
Conclusion. Onosma simplicissima L. demonstrates a high resource potential in the Novosibirsk Region and can be regarded as a promising source of phenolic compounds. Ecologically determined variability in biomass reserves and chemical composition does not limit the feasibility of sustainable harvesting across all studied sites. The obtained results may be applied in rational resource management and the development of phytomedicines.
Introduction. Virgin five-leaf grape (Parthenocissus quinquefolia (L.) Planch.) is a perennial wild or cultivated liana that is widespread. The plant is classified as understudied, which is why recommendations regarding optimal conditions for harvesting plant raw materials are still lacking. Currently, one of the key tasks in pharmacognosy is to identify new promising plant species among the representatives of the national flora that form a rich resource base. These species should be suitable for obtaining plant raw materials, which serve as the foundation for phytomedicines and/or dietary supplements. This underscores the relevance of the present study.
Aim. Rationalization of the procurement process and the development of quality indicators for plant raw materials "Virgin five-leaf grape leaves".
Materials and methods. The study involved the five-leafed maiden grape leaves harvested in the Voronezh Region during various phenological phases of the plant's life. Tests aimed at developing quality indicators of the studied plant raw materials were performed according to the methods presented in the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation XV and the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation XIV editions.
Results and discussion. The rationality of harvesting virgin-leaf grapes during the phase of mass fruiting and reddening of the leaves is shown. It is proposed to collect plant raw materials with a petiole, no more than 5 cm in size, in order to avoid difficulties during drying. Acceptable admixtures to maiden grape leaves are leaves that have changed color, as well as other parts of the plant. Criteria for assessing the quality of a new type of vegetable raw material "Maiden five-leaf grape" are proposed: the amount of flavonoids in terms of rutin is at least 0.9 %; the content of the sum of anthocyanin compounds in terms of cyaniding-3-O-glycoside is not less than 7 %; extractive substances extracted with 70 % ethyl alcohol – not less than 25 %, extractive substances extracted with water – not less than 25 %.
Conclusion. Criteria for assessing the quality of a new type of vegetable raw material "Virgin five-leaf grape leaves" are proposed. The experimental data obtained in the framework of the study were used in the development of instructions for harvesting and drying virgin leaf grapes, which was introduced into the scientific and production activities of the Botanical Garden named after Professor Boris M. Kozo-Polyansky VSU.