EDITORIAL
We present to your attention an interview with the General Director of LLC "CPHA", the editor-in-chief of the journals "Drug development & registration" and "Herbarium", Doctor of Pharmaceutical Sciences Igor E. Shohin.
PHARMACEUTICAL BOTANY
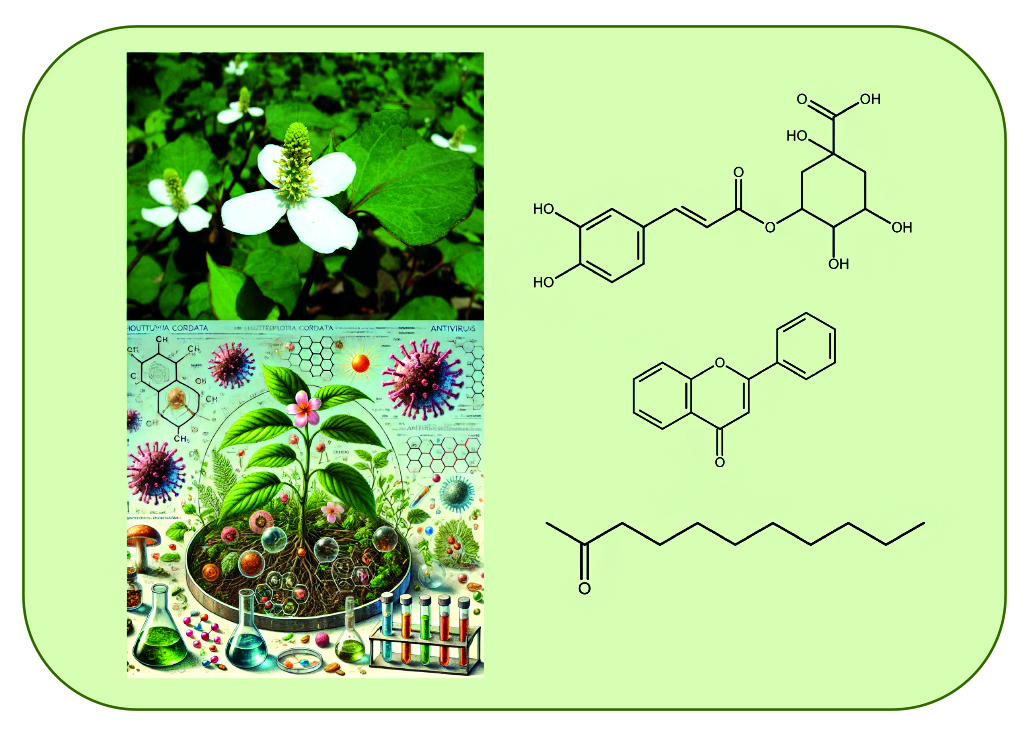
Introduction. The purpose of the review is to present new and summarized data on moprhology, ethnobotany, phytochemistry, and biological activity of the Houttuynia cordata Thunb. (Saururaceae), which is used in Asian folk medicine as a medical plant.
Text. Houttuynia cordata Thunb. Of the genus Saururaceae – a plant native to southeast Asia that grows in moist soil. In northeast India, it’s used extensively in cooking. Actively used in folk medicine.
Conclusion. The phytochemical analysis of the plant showed that composition of the plant includes ethereal oils, terpenoids, steroids, phenylpropanoids, phenolcarboxylic acids, glycosides, lignans/neolignans, flavonoids, phenanthrene derivatives, alkaloids, and other compounds. There is a review of content and distribution of the biomarker compounds as well as of study of extracts and various isolated compounds of wide range of biological activities including powerful antiviral properties (such as flavonoids) acting against a range of viruses (such as HSV-1, H1N1, and DENV) and such coronaviridaes as SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. Bioavailability of the plant raw materials, lack of toxicity, wide range of biological activities, and therapeutic potential require further target study of the Houttuynia cordata to determine the prospect of using of the herb as modern medicinal plant raw material.
ANALYSIS AND STANDARDIZATION OF MEDICINAL PLANT MATERIALS
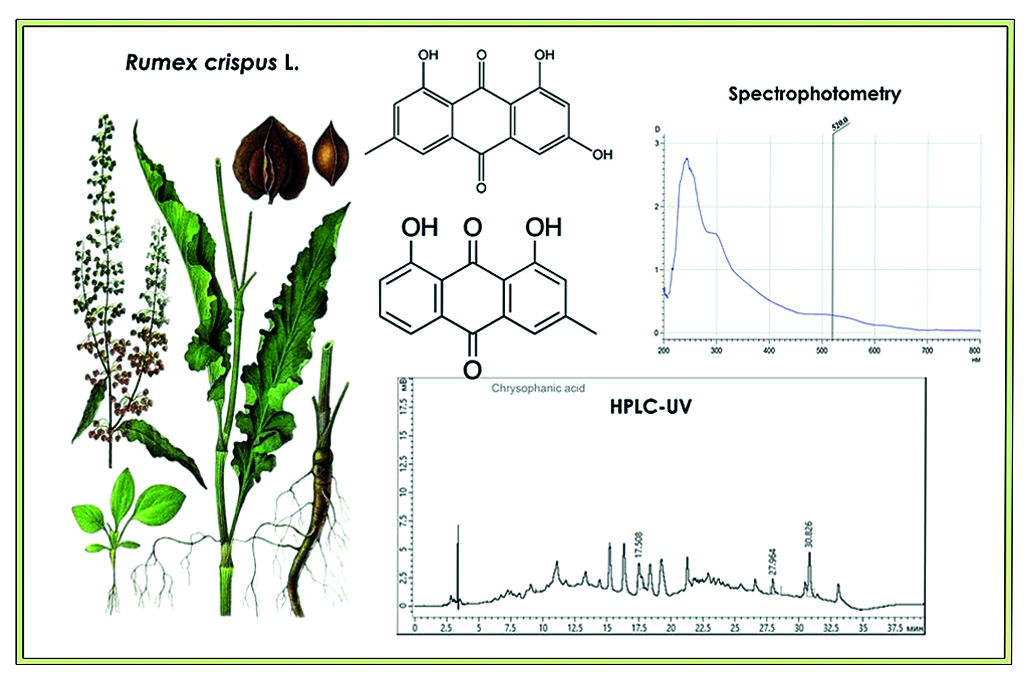
Introduction. At the moment, only one is included in the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation a representative of the Rumex genus is Rumex confertus Willd. Therefore, other representatives of this genus attracted our attention and Rumex criptus L. was studied in more detail. An important task is to determine the similarity of composition within the framework of expanding the raw material base.
Aim. Determination of the qualitative and quantitative content of anthraquinones in the roots of a representative of the genus Rumex (R. crispus).
Materials and methods. Alcohol extracts of underground organs were used as analyzed solutions R. crispus. Chromatographic separation and detection were carried out on a high-performance liquid chromatograph "Chromatek-Kristall HPLC 2014" (JSC SKB "Khromatek", Russia), equipped with a column thermostat, chromatographic column Grace HPLC Column Platinum C18-EPS, 250 × 4.6 mm, 5 µm (Grace, USA). Quantitative determination was carried out on an SF-2000 spectrophotometer (LLC "OKB Spektr", Russia).
Results and discussion. In the work, the object of study was Rumex criptus L., which contains a large amount of biologically active substances. In the roots of Rumex criptus L., anthracene derivatives, such as emodin-8-glycoside, emodin, chrysophanic acid, were identified and quantified by HPLC-UV, and the total amount of anthracene derivatives was determined by spectrophotometry.
Conclusion. The total content of anthracene derivatives in the underground organs of R. crispus L. in the dying phase is 4.953 %. Using HPLC-UV, emodin was determined, the quantitative content of which was 0.198 %, and chrysophanol, with a content of 0.757 %.
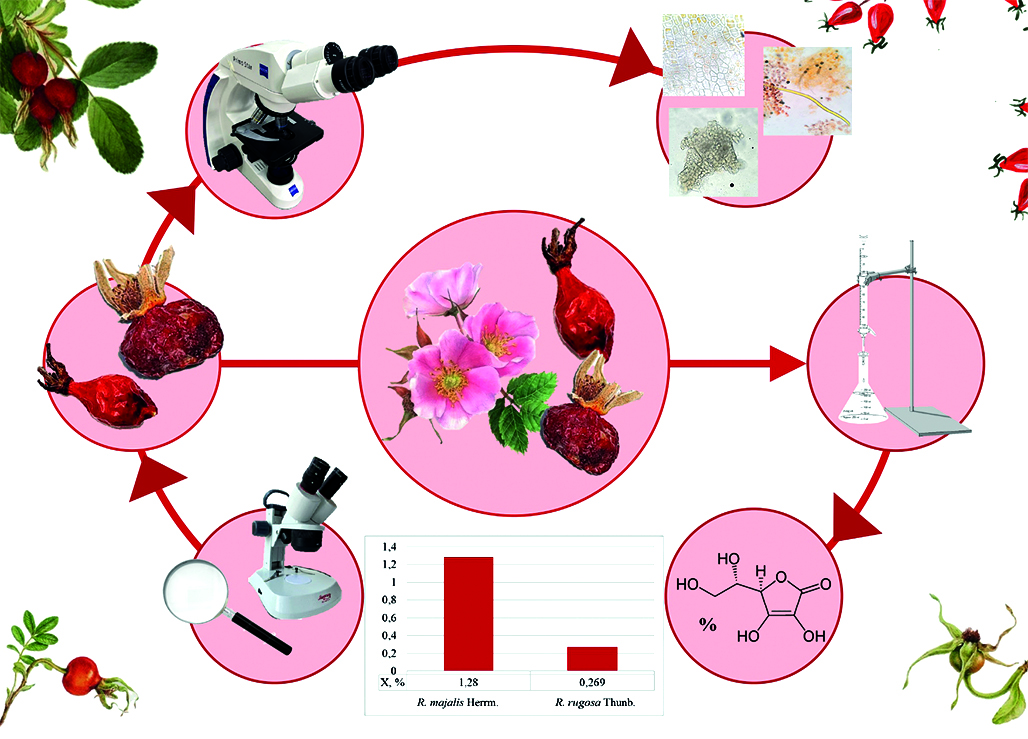
Introduction. Plants of the genus Rosa L. are widely used in folk and official medicine for the treatment of many diseases. The main pharmacological effects are achieved due to the rich complex of biologically active substances (BAS) contained in the fruits. According to the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation (SP RF) XV edition, the raw material of rose hips is the fruits of high-vitamin and low-vitamin species. It is of interest to estimate the quantitative content of biologically active substances in rose hips growing on the territory of the Russian Federation in order to expand the procurement sites for types of raw materials included in the pharmacopoeia.
Aim. Comparative analysis of external and microscopic characteristics of high-vitamin fruits of R. majalis Herrm. (R. cinnamomea L.) and R. rugosa Thunb., harvested in the Saratov region, as well as an assessment of the ascorbic acid content in them.
Materials and methods. The objects of the study were the fruits of the R. majalis Herrm. and the R. rugosa Thunb., harvested in October 2023 in the Saratov region. Macro- and microscopic analysis was performed using a Mikromed MS-1 stereomicroscope (China), a Primo Star microscope (Carl Zeiss AG, Germany) equipped with a Levenhuk M1400 PLUS digital camera, microphotography was edited in Photoscape 3.7 according to the requirements of the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation, XV edition. Quantitative determination of ascorbic acid was carried out by the titrimetric method in accordance with GPA.2.5.0106.18 «Rosae fructus» of the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation, XV edition. All experiments were performed in triplicate and statistically processed using MS Excel 2021.
Results and discussion. As a result of the conducted studies, the macro- and microscopic characteristics of the analyzed species correspond to the description given in GPA.2.5.0106.18 «Rosae fructus». In addition, we have clarified the macroscopic characteristics for each species, which can be used to confirm the authenticity of these species. The analysis showed that the content of ascorbic acid in the fruits of the R. majalis – 1.28 ± 0.05 % and in the R. rugosa – 0.27 ± 0.01 %, which meets the requirements of the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation XV edition for high-vitamin types of raw materials. The content of ascorbic acid in the fruits of the R. rugosa is comparable with the literature data from other regions of procurement, and in the fruits of the R. majalis the content is higher.
Conclusion. Analysis of fruits of R. majalis Herrm. and R. rugosa Thunb. revealed a high content of ascorbic acid, which makes it possible to procure these types of raw materials that meet the requirements of regulatory documentation in the Saratov region.
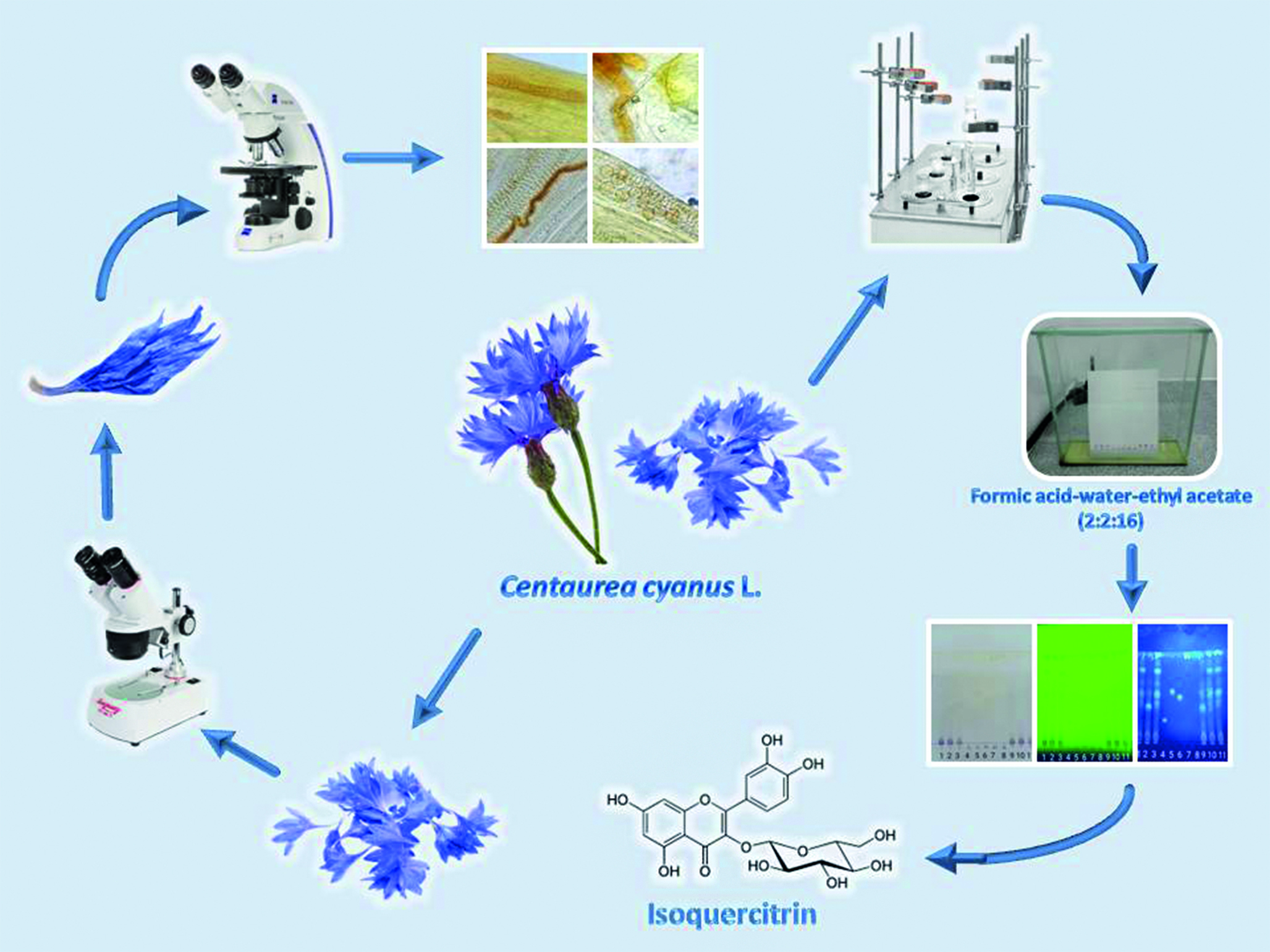
Introduction. Centaurea cyanus L. is an annual herbaceous plant whose funnel-shaped flowers are used as medicinal plant raw materials in official medicine. The biological activity (diuretic, choleretic, anti-inflammatory) of Centaurea cyanus flowers is associated with a complex of biologically active substances of phenolic nature. Anthocyanins act as the leading group used for the standardization of raw materials, according to the requirements of the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation, XV edition. Studies of the composition of flavonoids and phenolpropanoids of Centaurea cyanus flowers are relevant in terms of the value of their pharmacological properties.
Aim. To conduct TLC screening of phenolic compounds (flavonoids and phenolpropanoids) of Centaurea cyanus L. flowers.
Materials and methods. The objects of the study were dried whole flowers of Centaurea cyanus manufactured by the following companies: LLC «Lekra-SET», «Russkie Korni», Fito Way, LLC «HORST Company», LLC «Travy Gornogo Kryma» and LLC «Travy Bashkirii». Macro- and microscopic analysis was performed using a Mikromed MS-1 stereomicroscope (China), a Primo Star (Carl Zeiss, Germany) equipped with a Levenhuk M1400 PLUS digital camera, and microphotography editing was performed in Photoscape 3.7 according to the requirements of the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation, 15th edition. Screening of phenolic compounds was performed on plates with a silica gel layer on an aluminum substrate (Silica gel 60 F254, Merck KGaA, Германия). Detection was carried out with a 10 g/l solution of aminoethyl ester of diphenylboronic acid in ethyl alcohol and a 50 g/l solution of macrogol 400 in ethyl alcohol. After detection, the chromatograms were viewed in daylight and UV light at wavelengths of 254 and 365 nm using a UFS-254/365 chromatographic irradiator (IMID LLC, Russia). The comparison solutions were the following: rutin, quercetin, isoquercitrin, hyperoside, and caffeic acid.
Results and discussion. As a result of the studies, the macro- and microscopic characteristics of the analyzed samples of Centaurea cyanus flowers corresponded to FS.2.5.0064.18 «Centaurea cyanus flowers». An adsorption zone with yellow-green fluorescence was found on the chromatogram of all the studied extracts, which, according to the Rf value, corresponds to the isoquercitrin RS. Chromatographic profiles of four of the six analyzed objects had 4 chromatographic adsorption zones related to flavonoids and phenolpropanoids. The samples of «Russkie Korni» and LLC «HORST Company» had only 3 zones, which is probably due to the low concentration of phenolic compounds in the plant material.
Conclusion. The screening of phenolic compounds (flavonoids and phenolpropanoids) of Centaurea cyanus flowers was carried out using the planar chromatography method. The chromatograms of water-alcohol extracts showed an adsorption zone corresponding to isoquercitrin RS, and there were also other adsorption zones with fluorescence in UV light.