EDITORIAL
On February 26–27, the annual two-day congress "Drug development and registration" will be held in Moscow. The topics of the congress traditionally cover all key stages of a drug's life cycle, from development to post-registration studies.
CHEMISTRY OF NATURAL COMPOUNDS
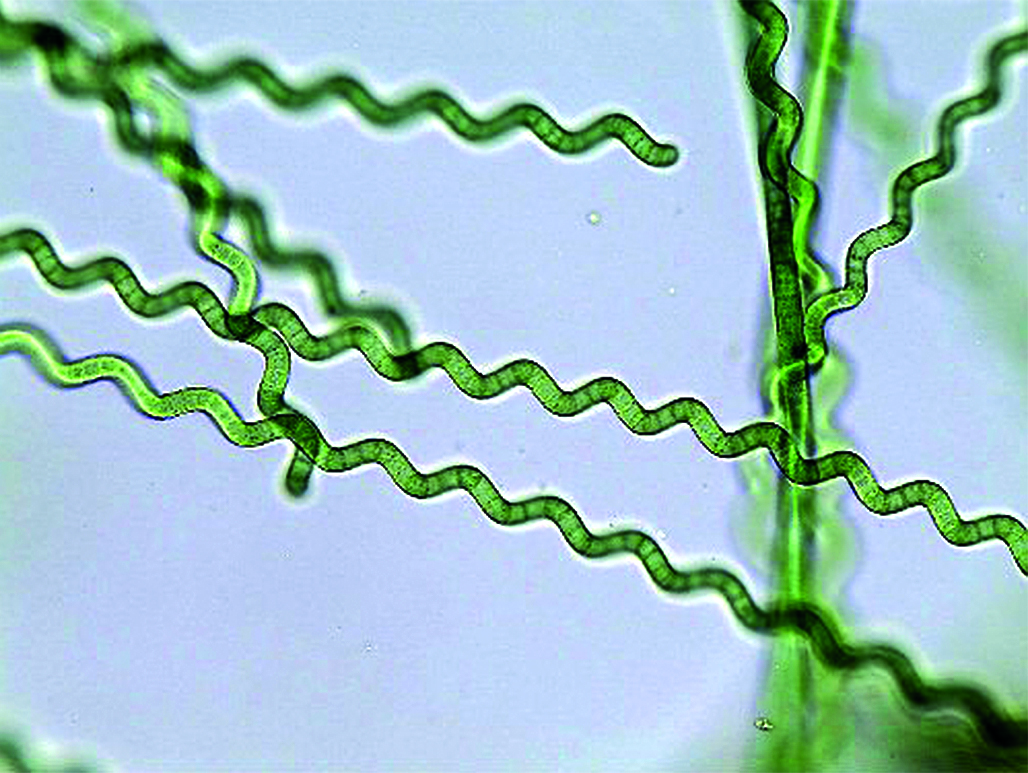
Introduction. Phycocyanin is a natural blue pigment found in spirulina that has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and antitumor properties.
Text. Phycobiliproteins, which are the main components of light-harvesting complexes in cyanobacteria and red algae, contain chromophores (phycobilins) that are covalently bound to protein subunits and are responsible for light absorption. These complexes form phycobilisomes capable of efficiently collecting and transferring light energy to photosynthetic reaction centers. Phycocyanin extraction requires the selection of a suitable cell destruction method in order to extract the protein while preserving its structure and function. Both physical and chemical methods can be used for this purpose. Subsequent purification includes several stages, during which ballast proteins and other impurities are removed. It may include fractionation with ammonium sulfate and a set of chromatographic methods. An important aspect is quality control, which is carried out using spectrophotometry. The stability of phycocyanin can change under the influence of various environmental factors such as light, temperature and pH. To increase its stability, stabilizers are used, which can act as mono- and disaccharides, as well as inorganic salts. Phycocyanin has a wide range of beneficial properties for the body, such as antioxidant activity, anti-inflammatory effect, protection of organs and tissues, as well as antitumor effect. It has virtually no toxic effect even at high doses, which opens up broad prospects for the development of new medicines.
Conclusion. Phycocyanin is a promising substance for medical use. However, there are difficulties associated with its extraction, purification and stabilization. In order to expand the scope of its application, further research is required aimed at developing more effective methods of preparation and stabilization.
ANALYSIS AND STANDARDIZATION OF MEDICINAL PLANT MATERIALS
Introduction. According to numerous studies, it is known that representatives of the genus Astragalus L. contain a variety of biologically active compounds: alkaloids, flavonoids, triterpene saponins, nitrogen-containing compounds, including amino acids, phenolic acids and their esters, coumarins, higher fatty acids, polysaccharides, vitamins B, C, E, PP, salts of glycyrrhizic acid, trace elements, tannins, essential oils, gums, etc. It is relevant to conduct a phytochemical analysis of herbs of new species of the genus Astragalus L., as well as screening the antioxidant activity of their extracts. The types of astragalus belonging to the Dissitiflori DC section can be a promising source of biologically active substances with an antioxidant effect.
Aim. To conduct a comparative phytochemical analysis and scoring of the antioxidant activity of aqueous extracts from the herb of four species of astragalus section Dissitiflori growing in the Saratov region.
Materials and methods. The objects of the study were dried herbs of Astragalus macropus Bunge, Astragalus zingeri Korsh., Astragalus varius S.G. Gmel. and Astragalus ucrainicus Klok. et M. Pop., collected in the Saratov region in 2023 and dried to a residual moisture content of no more than 14 %. The quantitative assessment of the content of tannins was carried out by the permanganometric method (titrant – 0.02 M potassium permanganate solution). The quantitative content of ascorbic acid was established by direct titration using a 0.0001 M solution of sodium 2,6-dichlorophenolindophenolate as a titrant. Antioxidant activity was determined by permanganometric titration in an acidic medium according to a patented technique. The antioxidant activity index was calculated in terms of flavonoid compounds known for their antioxidant activity: rutin, quercetin (mg/ml). Antiradical activity was assessed using the DPPH test. All analyses were performed in triplicate, the data were processed using standard statistical methods, using MS Excel packages, 2021.
Results and discussion. During the experiment, the herb of the genus Astragalus L. section Dissitiflori was analyzed for the content of tannins and ascorbic acid, and the antioxidant activity of extracts from the herb was determined by two methods. It was found that the highest content of tannins is observed in the herb A. macropus Bunge (2.27 ± 0.06 %) and A. zingeri Korsh. (2.23 ± 0.05 %); the highest content of ascorbic acid is in the herb A. varius S.G. Gmel. and A . zingeri Korsh. (0.04 ± 0.001 %). The highest antioxidant activity was observed in the extraction of A. ucrainicus Popov et Klok. from grass, which contains 23.03 ± 0.57 mg/g and 15.71 ± 0.39 mg/g of oxidizing substances in terms of rutin and quercetin, respectively, and antiradical activity in A. zingeri Korsh. (IC50 465.20 ± 12.2 mcg/ml).
Conclusion. Analysis of the grass of four species of the genus Astragalus L. section Dissitiflori revealed a high content of tannins and ascorbic acid, as well as the presence of pronounced antioxidant activity in extracts from the grass of the analyzed species.
BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY OF NATURAL SUBSTANCES
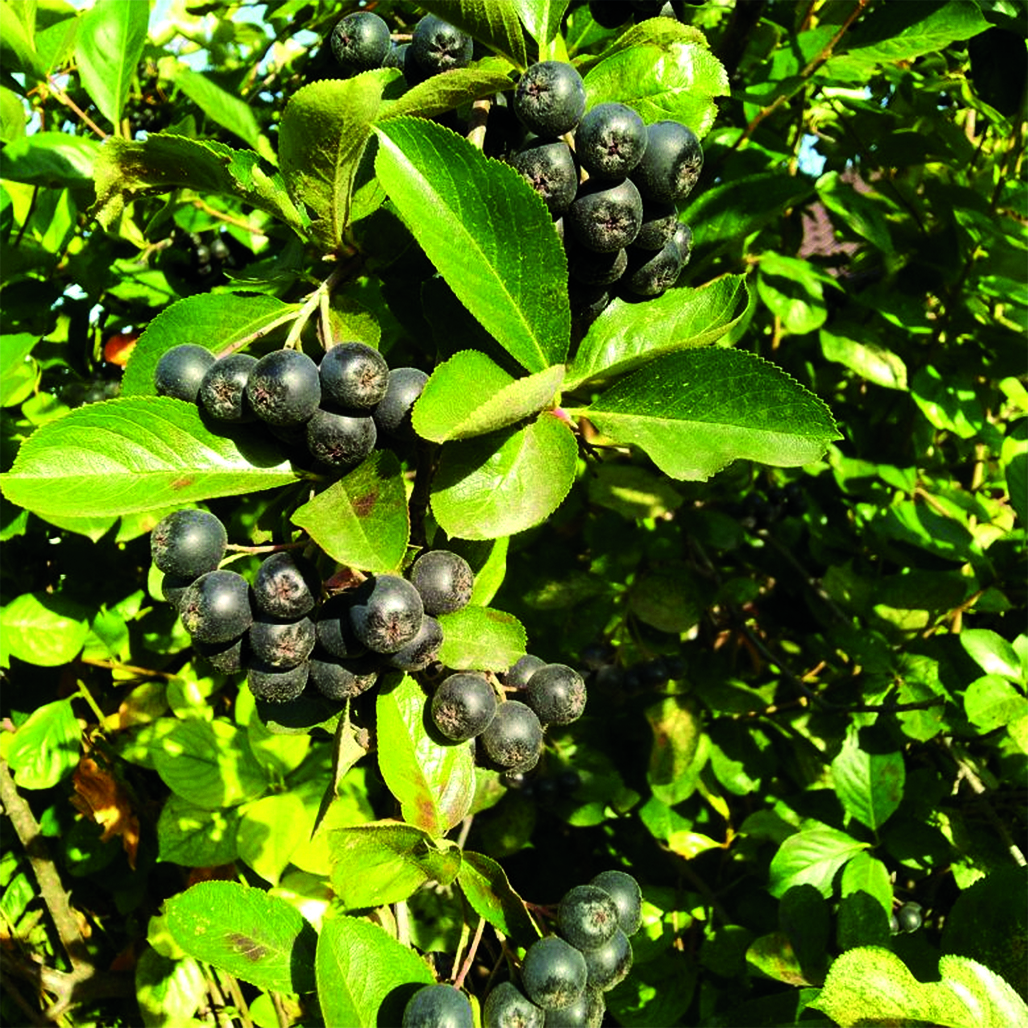
Introduction. Recently, researchers have shown great interest in studying the phytochemical composition of Michurin's aronia leaves (Aronia × mitschurinii A.K. Skvortsov & Maitul) due to the significant content of such valuable biologcally active substances (BAS) as flavonoids, leucoanthocyanins and tannins of the condensed group. Considering the high potential astringent, capillary-protective and anti-inflammatory activity of the main target groups of the BAS of the studied raw materials, in the framework of the present study we have analysed the antimicrobial activity of aqueous-alcoholic liquid extracts of the medicinal forms from Michurin's chokeberry leaves. In our recent studies, we have also established the biocidal effect of the decoction in vitro at a dilution of 1 : 10 on the test system of infusoria Parametium caudatum under the damaging effect of sodium chloride solution in the test "Functional load".
Aim. The purpose of the work was to determine the antimicrobial activity of aqueous-alcoholic liquid extraction dosage forms obtained from the leaves of chokeberry Michurin, in order to assess the prospects for creating medicinal herbal preparations (MHRP).
Materials and methods. The object of the study were liquid extraction dosage forms, tincture (1 : 5) and liquid extract (1 : 1), obtained from dried leaves of Michurin's chokeberry using 60 % ethanol. The antimicrobial activity of the samples was determined by the double serial dilution method. Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus cereus, Candida albicans, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains were used as test cultures. The prediction of the main types of pharmacological activity by in silico method was carried out for the pre-identified components of the leaf polyphenolic complex – catechin, rutin and leucocyanidin – using PassOnline and Phyto4Health platform. The medicinal forms obtained were standardised in accordance with the requirements for tinctures and extracts of the State Pharmacopoeia XV edition.
Results and discussion. The in silico screening of the main target groups of the BAS of the studied raw materials confirmed their high potential astringent and anti-inflammatory activity. The BAS complex of the liquid extract of Michurin's chokeberry leaves in comparison with the tincture shows antimicrobial activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa up to the 4th dilution and antifungal activity against Candida albicans up to the 6th dilution. In relation to such pathogenic microorganisms as Bacillus cereus and Staphylococcus aureus both tested dosage forms showed antimicrobial activity up to the 6th–7th dilution. The dosage form with a wider spectrum of antimicrobial activity is the liquid extract. In addition, the obtained dosage forms were standardized according to the requirements of the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation.
Conclusion. The results of the evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of the obtained alcoholic dosage forms based on Michurin's chokeberry leaves (tincture and liquid extract), confirmed the prospects of creating herbal medicines, e.g. for external use in the complex therapy and prevention of diseases of the oral cavity in the form of rinses or applications.
Introduction. The aim of the review is to summaries information on medicinal plants used in the prevention of respiratory diseases.
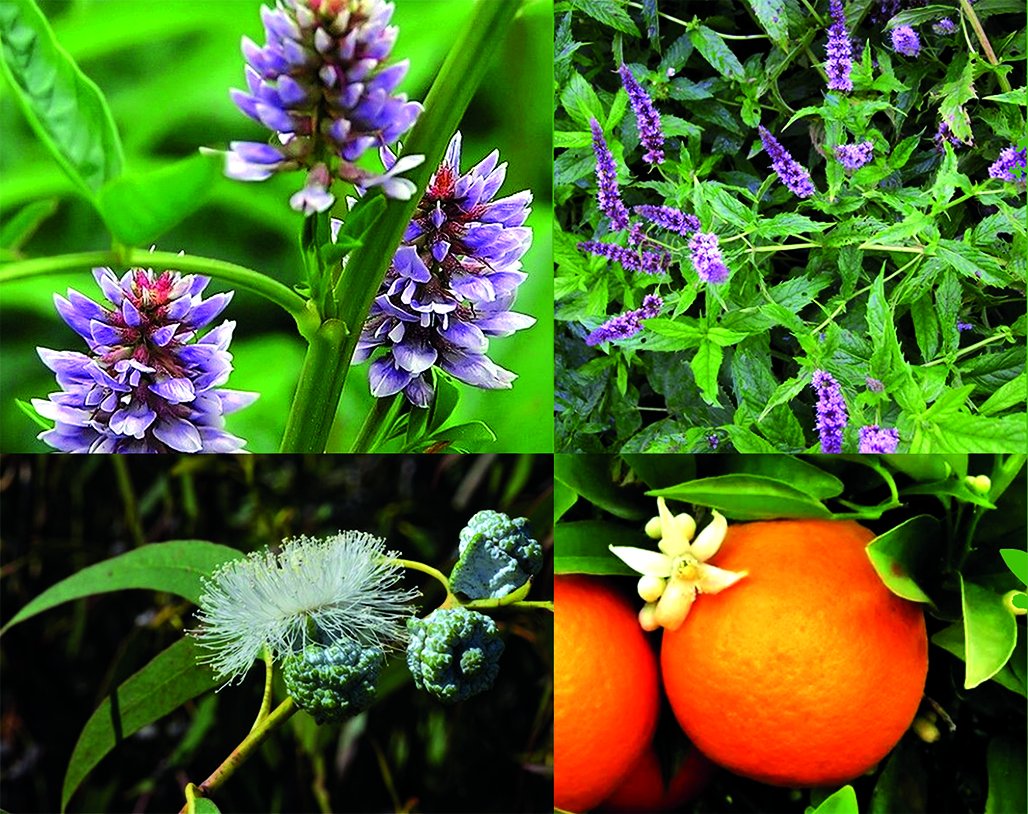
Text. According to Rosstat data, respiratory diseases occupy leading positions in the Russian Federation from year to year. For the treatment of acute respiratory diseases plant medicines are used, including Glycyrrhiza glabra L., Mentha spicata L., Eucalyptus globulus Labill., Citrus sinensis (L.) Pers., Cinnamomum camphora J. Presl.
Conclusion. The given extracts of medicinal plants have a long experience of application in traditional and scientific medicine, contain a complex of biologically active substances such as essential oils, saponins, polyphenols and polysaccharides with antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, analgesic and other effects that will allow in the complex therapy of acute tonsillopharyngitis, relieve the symptoms of the disease.